Though epicondylitis is also called Tennis elbow or Golfer’s elbow, depending on the specific location of the elbow joint affected, the incidence of this condition is not limited to sportspersons.
Here is a detailed discussion about what epicondylitis means and the types of epicondylitis. We will also discuss the causes, risk factors, and symptoms of this condition and learn the most effective ways to treat it.

What is Epicondylitis?
What is Lateral Epicondylitis?
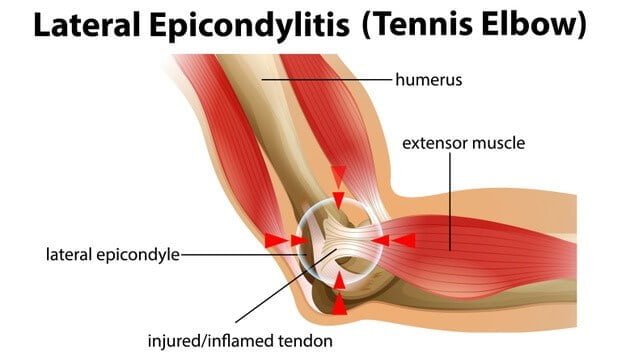
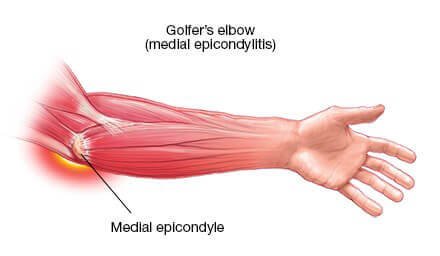
What is Medial Epicondylitis?
Epidemiology of Epicondylitis
What are the Causes of Epicondylitis?
- The risk of lateral epicondylitis is higher in people between the ages of 30 and 50 years.
- Lack of adequate warm-up before working out in the gym or performing strenuous activities can make the muscles and tendons more prone to microtears. This can increase the risk of lateral epicondylitis by causing more tissue damage.
- Following poor athletic techniques like using the force of the elbows instead of the core (abdominal) muscles could increase strain on the tissues of the elbow joints thus increasing the risk of the tennis elbow.
- Incorrect use of sports equipment like using too small or too large tennis rackets can increase the risk of lateral epicondylitis.
- Using a racket, which has not been strung properly or having its head surface too loose or too tight can also make you prone to develop this condition.
- Using a very heavy racket can create more strain on the muscles in the elbow thus triggering the development of the tennis elbow.
- Long-term use of some medications, including fluoroquinolone antibiotics, is one of the risk factors for this condition.
- The risk of this condition is comparatively higher in obese individuals and smokers.
- Lateral epicondylitis is considered idiopathic in nature when no apparent cause can be recognized.
Causes of Medial Epicondylitis
- Serving with greater force while playing tennis
- Exerting more strain on the elbow joint during a spin serve
- Weak wrist and shoulder muscles
- Using a tennis racket that is too tightly strung, too heavy, or too short
- Throwing a javelin
- Activities like chopping wood using an ax, operating a chain saw, or carrying heavy weights
What are the signs of Symptoms of Epicondylitis?
Symptoms of Medial Epicondylitis :
- Pain or burning sensation on the outer part of the elbow
- Weak grip strength
- Pain at night
- Elbow stiffness
- Tingling and numbness in the fingers, especially in the ring and little fingers
Diagnosis of Epicondylitis
Physical Examination
Your doctor will also ask questions about the history of recent injuries, your occupation, and the kinds of physical activities you perform to ascertain the cause of the tennis elbow or golfer’s elbow.
Your doctor will ask you to straighten your fingers and wrist against resistance while keeping your arm straight. If you experience severe pain during this movement, it could be a sign of epicondylitis.
Imaging tests
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is another imaging test that provides images of the soft tissues like muscles and tendons. An MRI scan will help to assess the extent of damage in the tendons to confirm the diagnosis of epicondylitis or rule out other causes like injuries.
An MRI scan of the neck may also be performed to rule out a herniated disk and arthritic changes in the neck both of which are known to cause pain in the arms.
The diagnosis of medial or lateral epicondylitis can be made based on the physical examination, medical and occupational history, and the results of these tests.
Treatment of Epicondylitis
Nonsurgical Treatment of epicondylitis
Rest
Ensuring your arm gets adequate rest is critical to faster recovery in patients with epicondylitis. It is advisable to limit your participation in sports or activities that involve excessive use of the elbow and wrists.
Medications
The use of acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen may be recommended to reduce pain and swelling in the affected tissues.
Brace
The use of a brace that is centered over the back of the forearm may relieve the symptoms of tennis elbow by stabilizing the muscles and tendons.
Steroid injections
Injections containing steroidal medications like cortisone can be effective in reducing inflammation in the affected region. The medications can be injected into the painful area around the lateral or medial epicondyle to relieve the symptoms.
Platelet-rich plasma
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) offers a biological treatment aimed at improving the internal biologic environment of the affected tissue.
It involves obtaining a sample of blood from your arm and centrifuging it to obtain platelets. These platelets contain a high concentration of growth factors that can stimulate healing when reinjected back into the affected tissues.
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy
This therapy involves the exposure of the tissues of the elbow to sound waves. The sound waves have the ability to create "microtrauma" that can stimulate the body's natural repair processes. This can accelerate healing and enable patients to recover faster.
Physical therapy
Specific exercises can be helpful for strengthening the forearm muscles. Ultrasound, muscle-stimulating techniques, and ice massage can be included in the treatment plan to accelerate muscle healing.
Surgical Treatment
If the symptoms do not respond to non-surgical treatments for more than 6 months, surgery may be needed to correct the damage.
Most surgical procedures for epicondylitis involve the removal of the damaged muscles and tendons and reattaching the healthy muscle tissues back to the bone.
Prognosis of Epicondylitis
However, it is important to adopt appropriate measures to prevent further damage to the elbow by changing the ways the wrists and forearms are used.
Limiting the activities that create more strain on the muscles of the elbow is highly recommended.
Also, patients should examine the tools or sports equipment they use and switch them with ergonomically suitable ones to ease the strain on the elbow. This would reduce damage to the muscles and improve the prognosis of epicondylitis.
If you are suffering from these symptoms, you can reach out to us to know more about lateral and medial epicondylitis. We can also discuss the possible diagnosis and the best treatment methods to help you overcome the symptoms and resume your activities in the shortest period.




